The first “super baby” born in the UK with the DNA of three people is a revolutionary achievement in science Today . This amazing achievement is the result of mitochondrial replacement therapy (MRT), or we can say a unique medical technique that focuses on preventing the transmission of exact genetic disorders from mother to child.
This baby’s birth stands for a significant milestone in reproductive medicine and provides hope for all families whoever child affected by genetic disorders. This article will go over the specifics of this innovative procedure and its Suggestion for the future of genetic engineering.
Now the birth of the UK’s first super baby not only highlights the potential of mitochondrial replacement therapy, but it also opens the door to wider conversations about the future of genetic engineering.
How genetic engineering are going to progress to prevent genetic disorders and MRT focuses on preventing Mitochondrial diseases, it not only opens the way for future advancements in human genetic changes but the procedure will be used in treatment of genetic deformities .
MRT (Mitochondrial Replacement Therapy)
:
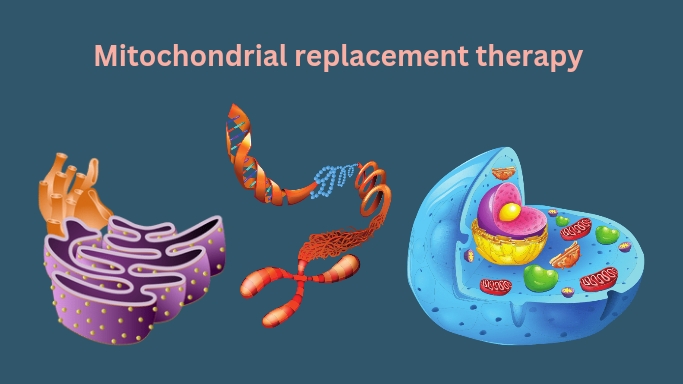
As we know that Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is only inherited from the mother and is responsible for producing energy into cells. in the form of ATP adenosine triphosphate and that produces energy.
But in a few mitochondrial genetic mutations can cause severe health problems in humans known as mitochondrial diseases, which may result in organ dysfunction and also premature death in infants or children. MRT will help to deal with this kind of issue by replacing the mother’s egg’s defective mitochondria with healthy mitochondria from a donor’s egg. Super baby
The Procedure for mitochondrial replacement therapy :
The mitochondrial replacement therapy process involves transferring the mother’s egg’s nuclear DNA to a donor egg that was treated with its nucleus eliminated but still has healthy mitochondria. This reconstructed egg, which contains nuclear DNA from the mother and healthy mitochondria from the donor, is then fertilized using in vitro fertilizations (IVF) mature eggs are collected from the mother’s ovaries and fertilized by sperm in a lab. after that fertilized egg (embryo) are transferred to a uterus. Or techniques in which with the father’s sperm. As a result, the resulting embryo inherits both parents’ nuclear DNA along with the donor’s healthy mitochondria.
Moral and proper considerations:
While the birth of a super baby with DNA from three people raises ethical and legal questions, the United Kingdom has been at the center of regulatory structures to ensure the protection and ethical principles of such procedures. The Human Fertilizations and Embryology Authority (HFEA) strictly regulates the use of MRT, allowing it only in cases where the risk of transmitting serious mitochondrial diseases is high. This strict control ensures that the technique is used responsibly and ethically, with the child’s and future generations’ well-being as top of mind.
in case if you are interested on this type of medico topic here are our top what is a zombie drug
Potential Advantages and Difficulties:
The birth of the UK’s first “super baby” opens up a new world of possibilities for preventing mitochondrial disease transmission. Families with these genetic disorders are frequently faced with the devastating decision if they want to have a child naturally and risk passing on the disease, or to follow other options, such as adoption or using donor eggs. MRT gives these families hope by giving them the opportunity to have children with a genetic connection that are free of mitochondrial diseases.
However it is critical to tackle the issues and potential difficulties related to this procedure. Individuals claim that MRT may open the way for “designer kids” and the manipulation of human biological characteristics for purposes other than disease prevention. MRT’s long-term effects remain unknown, and it is essential that ongoing investigation continues to monitor the health and psychological well-being of children born via this technique.
The birth of the UK’s first super baby, with three people’s DNA, marks a significant turning point in reproductive medicine. Mitochondrial replacement therapy gives children affected by mitochondrial illnesses because it allows them to have healthy children without the risk of passing on limiting genetic diseases. While this significant technique increases important ethical concerns, its controlled and responsible application may greatly help future generations. As science and medicine advance, it is critical to strike a balance between using the benefits of biotechnology and ensuring individuals’ well-being and independence.